|
Overview
 Flexible flatfeet are considered normal in young children because babies are not born with a normal arch. The arch may not form fully until sometime between ages 7 and 10. Even in adulthood, 15% to 25% of people have flexible flatfeet. Most of these people never develop symptoms. In many adults who have had flexible flatfeet since childhood, the missing arch is an inherited condition related to a general looseness of ligaments. These people usually have extremely flexible, very mobile joints throughout the body, not only in the feet. Flatfeet also can develop during adulthood. Causes include joint disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis, and disorders of nerve function (neuropathy). Unlike a flexible flatfoot, a rigid flatfoot is often the result of a significant problem affecting the structure or alignment of the bones that make up the foot's arch. Some common causes of rigid flatfeet include. Congenital vertical talus. In this condition, there is no arch because the foot bones are not aligned properly. In some cases, there is a reverse curve (rocker-bottom foot, in which the shape is like the bottom rails of a rocking chair) in place of the normal arch. Congenital vertical talus is a rare condition present at birth. It often is associated with a genetic disorder, such as Down syndrome, or other congenital disorders. The cause is unknown in up to half of cases. Tarsal coalition (peroneal spastic flatfoot). In this inherited condition, two or more of the foot bones are fused together, interfering with the flexibility of the foot and eliminating the normal arch. A rare condition, it often affects several generations of the same family. Lateral subtalar dislocation. Sometimes called an acquired flatfoot, it occurs in someone who originally had a normal foot arch. In a lateral subtalar dislocation, there is a dislocation of the talus bone, located within the arch of the foot. The dislocated talus bone slips out of place, drops downward and sideways and collapses the arch. It usually occurs suddenly because of a high-impact injury related to a fall from a height, a motor vehicle accident or participation in sports, and it may be associated with fractures or other injuries. Causes When flat feet develop at a later age, they are known as fallen arches. The arches may fall because the muscles supporting them are no longer able to do so. In addition the spring ligament within the foot may have lost some of its tension allowing the arch of the foot to flatten. Other conditions causing fallen arches include sudden weight gain, a nervous system injury, or a loss of sensation caused by a disease such as diabetes. Most people with fallen arches are flat on both feet. Symptoms Flat feet can cause a myriad of symptoms, from experiencing pain in the foot, heels, arch, calves, the shin, the knee, the hip and into the lower back due to overworking of the hip flexors or they may find it hard to stand on tip toes. Diagnosis Most children and adults with flatfeet do not need to see a physician for diagnosis or treatment. However, it is a good idea to see a doctor if the feet tire easily or are painful after standing, it is difficult to move the foot around or stand on the toes, the foot aches, especially in the heel or arch, and there is swelling on the inner side of the foot, the pain interferes with activity or the person has been diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. Most flatfeet are diagnosed during physical examination. During the exam, the foot may be wetted and the patient asked to stand on a piece of paper. An outline of the entire foot will indicate a flattened arch. Also, when looking at the feet from behind, the ankle and heel may appear to lean inward (pronation). The patient may be asked to walk so the doctor can see how much the arch flattens during walking. The doctor may also examine the patient's shoes for signs of uneven wear, ask questions about a family history of flatfeet, and inquire about known neurological or muscular diseases. Imaging tests may be used to help in the diagnosis. If there is pain or the arch does not appear when the foot is flexed, x-rays are taken to determine the cause. If tarsal coalition is suspected, computed tomography (CT scan) may be performed, and if an injury to the tendons is suspected, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI scan) may be performed. pes valgus Non Surgical Treatment Treatment for flat feet and fallen arches depends on the severity and cause of the problem. If flat feet cause no pain or other difficulties, then treatment is probably not needed. In other cases, your doctor may suggest one or more of these treatments. Rest and ice to relieve pain and reduce swelling, stretching exercises, pain relief medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories, physical therapy, orthotic devices, shoe modifications, braces, or casts, injected medications to reduce inflammation, such as corticosteroids. If pain or foot damage is severe, your doctor may recommend surgery. Surgical Treatment  Feet that do not respond to the treatments above may need surgery. The surgery will help to create a supportive arch. After Care Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon. Overview
 The heel bone is the largest of the 26 bones in the human foot, which also has 33 joints and a network of more than 100 tendons, muscles, and ligaments. Like all bones, it is subject to outside influences that can affect its integrity and its ability to keep us on our feet. Heel pain, sometimes disabling, can occur in the front, back, or bottom of the heel. Causes Near the inflamed plantar fascia attachment, but not in it, some extra bone may form, producing a small "spur". In fact, it is a shelf of bone, not a sharp spur. These "heel spurs" are commoner in people with plantar fascitis, but they can be found in people with no heel pain. The heel spur is caused by the same process as the heel pain, but the spur is not itself the cause of the pain. Symptoms See your doctor immediately if you have Severe pain and swelling near your heel. Inability to bend your foot downward, rise on your toes or walk normally. Heel pain with fever, numbness or tingling in your heel. Severe heel pain immediately after an injury. Schedule an office visit if you have. Heel pain that continues when you're not walking or standing. Heel pain that lasts more than a few weeks, even after you've tried rest, ice and other home treatments. Diagnosis After you have described your foot symptoms, your doctor will want to know more details about your pain, your medical history and lifestyle, including. Whether your pain is worse at specific times of the day or after specific activities. Any recent injury to the area. Your medical and orthopedic history, especially any history of diabetes, arthritis or injury to your foot or leg. Your age and occupation. Your recreational activities, including sports and exercise programs. The type of shoes you usually wear, how well they fit, and how frequently you buy a new pair. Your doctor will examine you, including. An evaluation of your gait. While you are barefoot, your doctor will ask you to stand still and to walk in order to evaluate how your foot moves as you walk. An examination of your feet. Your doctor may compare your feet for any differences between them. Then your doctor may examine your painful foot for signs of tenderness, swelling, discoloration, muscle weakness and decreased range of motion. A neurological examination. The nerves and muscles may be evaluated by checking strength, sensation and reflexes. In addition to examining you, your health care professional may want to examine your shoes. Signs of excessive wear in certain parts of a shoe can provide valuable clues to problems in the way you walk and poor bone alignment. Depending on the results of your physical examination, you may need foot X-rays or other diagnostic tests. Non Surgical Treatment Treatment for heel pain usually involves using a combination of techniques, such as stretches and painkillers, to relieve pain and speed up recovery. Most cases of heel pain get better within 12 months. Surgery may be recommended as a last resort if your symptoms don't improve after this time. Only 1 in 20 people with heel pain will need surgery. Whenever possible, rest the affected foot by not walking long distances and standing for long periods. However, you should regularly stretch your feet and calves using exercises such as those described. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, can be used to help relieve pain. Some people also find applying an ice pack to the affected heel for 5-10 minutes can help relieve pain and inflammation. However, do not apply an ice pack directly to your skin. Instead, wrap it in a towel. If you do not have an ice pack, you can use a packet of frozen vegetables. Exercises designed to stretch both your calf muscles and your plantar fascia (the band of tissue that runs under the sole of your foot) should help relieve pain and improve flexibility in the affected foot. A number of stretching exercises are described below. It's usually recommended that you do the exercises on both legs, even if only one of your heels is affected by pain. This will improve your balance and stability, and help relieve heel pain. Keep a long towel beside your bed. Before you get out of bed in the morning, loop the towel around your foot and use it to pull your toes towards your body, while keeping your knee straight. Repeat three times on each foot. Place both hands on a wall at shoulder height, with one of your feet in front of the other. The front foot should be about 30cm (12 inches) away from the wall. With your front knee bent and your back leg straight, lean towards the wall until you feel a tightening in the calf muscles of your back leg. Then relax. Repeat this exercise 10 times before switching legs and repeating the cycle. You should practise wall stretches twice a day. Stand on a step of your stairs facing upstairs, using your banister for support. Your feet should be slightly apart, with your heels hanging off the back of the step. Lower your heels until you feel a tightening in your calves. Hold this position for about 40 seconds, before raising your heels back to the starting position. Repeat this procedure six times, at least twice a day. Sit on a chair, with your knees bent at right angles. Turn your feet sideways so your heels are touching and your toes are pointing in opposite directions. Lift the toes of the affected foot upwards, while keeping the heel firmly on the floor. You should feel your calf muscles and Achilles tendon (the band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your calf muscle) tighten. Hold this position for several seconds and then relax. Repeat this procedure 10 times, five to six times a day. While seated, roll the arch of your foot (the curved bottom part of the foot between your toes and heel) over a round object, such as a rolling pin, tennis ball or drinks can. Some people find that using a chilled can from their fridge has the added benefit of helping to relieve pain. Move your foot and ankle in all directions over the object for several minutes. Repeat the exercise twice a day. Your GP or podiatrist may advise you to change your footwear. You should avoid wearing flat-soled shoes, because they will not provide your heel with support and could make your heel pain worse. Ideally, you should wear shoes that cushion your heels and provide a good level of support to the arches of your feet. For women wearing high heels, and for men wearing heeled boots or brogues, can provide short- to medium-term pain relief, as they help reduce pressure on the heels. However, these types of shoes may not be suitable in the long term, because they can lead to further episodes of heel pain. Your GP or podiatrist can advise on footwear. Orthoses are insoles that fit inside your shoe to support your foot and help your heel recover. You can buy orthoses off-the-shelf from sports shops and larger pharmacies. Alternatively, your podiatrist should be able to recommend a supplier. If your pain does not respond to treatment and keeps recurring, or if you have an abnormal foot shape or structure, custom-made orthoses are available. These are specifically made to fit the shape of your feet. However, there is currently no evidence to suggest that custom-made orthoses are more effective than those bought off-the-shelf. An alternative to using orthoses is to have your heel strapped with sports strapping (zinc oxide) tape, which helps relieve pressure on your heel. Your GP or podiatrist can teach you how to apply the tape yourself. In some cases, night splints can also be useful. Most people sleep with their toes pointing down, which means tissue inside the heel is squeezed together. Night splints, which look like boots, are designed to keep your toes and feet pointing up while you are asleep. This will stretch both your Achilles tendon and your plantar fascia, which should help speed up your recovery time. Night splints are usually only available from specialist shops and online retailers. Again, your podiatrist should be able to recommend a supplier. If treatment hasn't helped relieve your painful symptoms, your GP may recommend corticosteroid injections. Corticosteroids are a type of medication that have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect. They have to be used sparingly because overuse can cause serious side effects, such as weight gain and high blood pressure (hypertension). As a result, it is usually recommended that no more than three corticosteroid injections are given within a year in any part of the body. Before having a corticosteroid injection, a local anaesthetic may be used to numb your foot so you don't feel any pain. Surgical Treatment At most 95% of heel pain can be treated without surgery. A very low percentage of people really need to have surgery on the heel. It is a biomechanical problem and it?s very imperative that you not only get evaluated, but receive care immediately. Having heel pain is like having a problem with your eyes; as you would get glasses to correct your eyes, you should look into orthotics to correct your foot. Orthotics are sort of like glasses for the feet. They correct and realign the foot to put them into neutral or normal position to really prevent heel pain, and many other foot issues. Whether it be bunions, hammertoes, neuromas, or even ankle instability, a custom orthotic is something worth considering. no foot pain Prevention  A variety of steps can be taken to avoid heel pain and accompanying afflictions. Wear shoes that fit well-front, back, and sides-and have shock-absorbent soles, rigid shanks, and supportive heel counters. Wear the proper shoes for each activity. Do not wear shoes with excessive wear on heels or soles. Prepare properly before exercising. Warm up and do stretching exercises before and after running. Pace yourself when you participate in athletic activities. Don?t underestimate your body's need for rest and good nutrition. If obese, lose weight. Overview
Surgical treatments vary in complexity. Sometimes the goal of surgery is to stop the growth of the longer limb. Other times, surgeons work to lengthen the shorter limb. Orthopedic surgeons may treat children who have limb-length conditions with one or a combination of these surgical techniques. Bone resection. An operation to remove a section of bone, evening out the limbs in teens or adults who are no longer growing. Epiphyseal stapling. An operation to slow the rate of growth of the longer limb by inserting staples into the growth plate, then removing them when the desired result is achieved. Epiphysiodesis. An operation to slow the rate of growth of the longer limb by creating a permanent bony ridge near the growth plate. Limb lengthening. A procedure (also called distraction osteogenesis or the Ilizarov procedure) that involves attaching an internal or external fixator to a limb and gradually pulling apart bone segments to grow new bone between them. There are several ways your doctor can predict the final LLD, and thus the timing of the surgery. The easiest way is the so-called Australian method, popularised by Dr. Malcolm Menelaus, an Australian orthopedic surgeon. According to this method, growth in girls is estimated to stop at age 14, and in boys at age 16 years. The femur grows at the rate of 10 mm. a year, and the upper tibia at the rate of 6 mm. a year. Using simple arithmetic, one can get a fairly good prediction of future growth. This of course, is an average, and the patient may be an average. To cut down the risk of this, the doctor usually measures leg length using special X-ray technique (called a Scanogram) on three occasions over at least one year duration to estimate growth per year. He may also do an X-ray of the left hand to estimate the bone age (which in some cases may differ from chronological age) by comparing it with an atlas of bone age. In most cases, however, the bone age and chronological age are quite close. Another method of predicting final LLD is by using Anderson and Green?s remaining growth charts. This is a very cumbersome method, but was till the 1970?s, the only method of predicting remaining growth. More recently, however, a much more convenient method of predicting LLD was discovered by Dr. Colin Moseley from Montreal. His technique of using straight line graphs to plot growth of leg lengths is now the most widely used method of predicting leg length discrepancy. Whatever method your doctor uses, over a period of one or two years, once he has a good idea of the final LLD, he can then formulate a plan to equalize leg lengths. Epiphyseodesis is usually done in the last 2 to 3 years of growth, giving a maximum correction of about 5 cm. Leg lengthening can be done at any age, and can give corrections of 5 to10 cm., or more.  Causes Sometimes the cause of LLD is unknown, yet the pattern or combination of conditions is consistent with a certain abnormality. Examples include underdevelopment of the inner or outer side of the leg (hemimelias) or (partial) inhibition of growth of one side of the body of unknown cause (hemihypertrophy). These conditions are present at birth, but the limb length difference may be too small to be detected. As the child grows, the LLD increases and becomes more noticeable. In hemimelia, one of the two bones between the knee and the ankle (tibia or fibula) is abnormally short. There also may be associated foot or knee abnormalities. Hemihypertrophy or hemiatrophy are rare conditions in which there is a difference in length of both the arm and leg on only one side of the body. There may also be a difference between the two sides of the face. Sometimes no cause can be found. This type of limb length is called idiopathic. While there is a cause, it cannot be determined using currect diagnostic methods. Symptoms Often there are few or no symptoms prior to the age of 25-35. The most common symptom is chronic lower back pain, but also is frequently middle and upper back pain. Same-sided and repeated injury or pain to the hip, knee and/or ankle is also a hallmark of a long-standing untreated LLD. It is not uncommon to have buttock or radiating hip pain that is non-dermatomal (not from a disc) and tends to go away when lying down. Diagnosis On standing examination one iliac crest may be higher/lower than the other. However a physiotherapist, osteopath or chiropractor will examine the LLD in prone or supine position and measure it, confirming the diagnosis of structural (or functional) LLD. The LLD should be measured using bony fixed points. X-Ray should be taken in a standing position. The osteopath, physiotherapist or chiropractor will look at femoral head & acetabulum, knee joints, ankle joints. Non Surgical Treatment Treatment depends on what limb has the deformity and the amount of deformity present. For example, there may be loss of function of the leg or arm. Cosmetic issues may also be a concern for the patient and their family. If there are problems with the arms, the goal is to improve the appearance and function of the arm. Treatment of leg problems try to correct the deformity that may cause arthritis as the child gets older. If the problem is leg length, where the legs are not "equal," the goal is equalization (making the legs the same length). Treatment may include the use of adaptive devices, prosthesis, orthotics or shoe lifts. If the problem is more severe and not treatable with these methods, then surgery may be necessary. shoe lifts for men's shoes Surgical Treatment Leg shortening is employed when LLD is severe and when a patient has already reached skeletal maturity. The actual surgery is called an osteotomy , which entails the removal of a small section of bone in the tibia (shinbone) and sometimes the fibula as well, resulting in the loss of around an inch in total height. Leg lengthening is a difficult third option that has traditionally had a high complication rate. Recently, results have improved somewhat with the emergence of a technique known as callotasis , in which only the outer portion of the bone (the cortex ) is cut, (i.e. a corticotomy ). This allows the bone to be more easily lengthened by an external fixation device that is attached to either side of the cut bone with pins through the skin. The ?ex-fix,' as it is sometimes called, is gradually adjusted by an orthopaedic surgeon, and healing can occur at the same time that the leg is being distracted , or lengthened over time. Unlike epiphysiodesis, leg lengthening procedures can be performed at almost any skeletal or chronological age. Overview
 Morton's neuroma is a painful foot condition that occurs when a nerve, usually between the third and fourth toes, expands and becomes compressed. Shoes, particularly high heels or shoes with tight toe boxes, and walking often make the pain worse. In some cases, patients with Morton's neuroma find short-term pain relief when they do not put weight on the affected foot. Morton's neuroma is a painful foot condition that occurs when a nerve, usually between the third and fourth toes, expands and becomes compressed. Shoes, particularly high heels or shoes with tight toe boxes, and walking often make the pain worse. In some cases, patients with Morton's neuroma find short-term pain relief when they do not put weight on the affected foot.Causes Some experts believe that other foot conditions may also be associated with Morton's neuroma. This is because other conditions may cause the metatarsal bones to rub against the nerve in your foot. Foot problems that may increase your risk of developing Morton's neuroma include abnormally positioned toes, high arches, where the arch or instep of your foot is raised more than normal, flat feet, low arches or no arches at all, bunions a bony swelling at the base of the toe. Hammer toe, where the toe is bent at the middle joint. Being active and playing sport can make the painful symptoms of Morton's neuroma worse. In particular, running or sports that involve running, such as racquet sports, can place extra pressure on the nerve in your foot, which can aggravate the problem. Symptoms Outward signs of Morton's neuroma, such as a lump, are extremely rare. Morton's neuroma signs and symptoms, which usually occur unexpectedly and tend to worsen over time, include, pain on weight bearing (while walking) - a shooting pain affecting the contiguous halves of two toes, which may be felt after only a short time (of weight bearing). Sometimes there may be a dull pain rather than a sharp one. Most commonly, pain is felt between the third and fourth toes. Typically, a patient will suddenly experience pain while walking and will have to stop and remove their shoe. Burning. Numbness. Parasthesia, tingling, pricking, or numbness with no apparent long-term physical effect. Commonly known as pins-and-needles. A sensation that something is inside the ball of the foot. Diagnosis The clinical symptoms should quickly lead your doctor to suspect a neuroma. When examined, the doctor may feel a "click" which is known as Mulder's sign. There may be tenderness in the interspace. The metatarsal bones will also be examined both clinically (and often with an xray). Tenderness at one of the metatarsal bones can suggest an overstress reaction (pre-stress fracture or stress fracture) in the bone. An ultrasound scan can confirm the diagnosis and is a less expensive and at this time, at least as sensitive a test as an MRI. An x-ray does not show neuromas, but can be useful to "rule out" other causes of the pain. Non Surgical Treatment Relief of symptoms can often start by having a good pair of well fitting shoes fitted to your feet ensuring that the shoes don't squeeze your foot together. Once footwear is addressed patients may require a small pre-metatarsal pad to be positioned onto the insole of the shoe to help lift and separate the bones in the forefoot to alleviate the pressure on the nerve. If the patients foot structure and mechanics is found to be a contributing cause, a custom made orthotic is usually the most convenient and effective way to manage the problem. Sometimes an injection of local anaesthetic and steroid is recommended to assist in settling acute symptoms.  Surgical Treatment Surgical treatment has provided relief in some cases while poor results and surgical complications have resulted in other cases. It is believed that ligament weakness, as opposed to the pinching of nerves in the foot, may be to blame for recurrent pain in these situations. For reasons which are not fully understood, the incidence of Morton?s Neuroma is 8 to 10 times greater in women than in men. There are actually two different kinds of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital indicates you are born with it. One leg is anatomically shorter than the other. Through developmental periods of aging, the brain senses the gait pattern and recognizes some variation. The human body usually adapts by dipping one shoulder to the "short" side. A difference of less than a quarter inch isn't really abnormal, demand Shoe Lifts to compensate and generally does not have a serious effect over a lifetime.
 Leg length inequality goes largely undiscovered on a daily basis, yet this problem is easily corrected, and can eradicate a number of cases of back ache. Therapy for leg length inequality typically consists of Shoe Lifts. These are low cost, ordinarily costing less than twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 and up. When the amount of leg length inequality begins to exceed half an inch, a whole sole lift is generally the better choice than a heel lift. This prevents the foot from being unnecessarily stressed in an abnormal position. Mid back pain is easily the most widespread ailment affecting men and women today. Over 80 million men and women suffer from back pain at some point in their life. It's a problem that costs employers huge amounts of money every year because of lost time and productivity. Fresh and more effective treatment solutions are constantly sought after in the hope of decreasing the economic impact this issue causes.  People from all corners of the world suffer from foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these situations Shoe Lifts might be of very helpful. The lifts are capable of eliminating any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless experienced orthopaedic doctors. In order to support the human body in a healthy and balanced manner, feet have a vital task to play. Despite that, it is often the most neglected area of the body. Some people have flat-feet which means there is unequal force exerted on the feet. This will cause other body parts including knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that correct posture and balance are restored. There are not one but two unique variations of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital indicates that you are born with it. One leg is structurally shorter than the other. Through developmental periods of aging, the human brain picks up on the stride pattern and identifies some difference. The human body typically adapts by dipping one shoulder to the "short" side. A difference of under a quarter inch isn't really abnormal, demand Shoe Lifts to compensate and in most cases doesn't have a serious effect over a lifetime.
 Leg length inequality goes mainly undiscovered on a daily basis, however this problem is very easily corrected, and can eliminate a number of instances of upper back pain. Treatment for leg length inequality usually consists of Shoe Lifts. Many are economical, frequently priced at below twenty dollars, compared to a custom orthotic of $200 or higher. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe. Low back pain is the most common condition afflicting people today. Around 80 million men and women are affected by back pain at some stage in their life. It's a problem that costs businesses huge amounts of money each year as a result of time lost and productivity. New and superior treatment methods are continually sought after in the hope of lowering economical impact this issue causes.  Men and women from all corners of the earth suffer from foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In most of these cases Shoe Lifts might be of very beneficial. The lifts are capable of eliminating any discomfort and pain in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by numerous skilled orthopaedic orthopedists. So that you can support the human body in a well-balanced fashion, feet have got a very important job to play. Irrespective of that, it is often the most overlooked area of the human body. Many people have flat-feet which means there is unequal force placed on the feet. This causes other body parts such as knees, ankles and backs to be affected too. Shoe Lifts ensure that proper posture and balance are restored. There are two unique variations of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital indicates you are born with it. One leg is anatomically shorter than the other. Through developmental phases of aging, the brain picks up on the gait pattern and identifies some difference. The entire body typically adapts by tilting one shoulder to the "short" side. A difference of under a quarter inch is not very uncommon, does not need Shoe Lifts to compensate and commonly does not have a profound effect over a lifetime.
 Leg length inequality goes largely undiagnosed on a daily basis, however this condition is simply remedied, and can reduce many instances of lumbar pain. Treatment for leg length inequality typically consists of Shoe Lifts. They are low-priced, typically being less than twenty dollars, compared to a custom orthotic of $200 and up. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe. Low back pain is easily the most prevalent condition afflicting people today. Over 80 million men and women are afflicted by back pain at some stage in their life. It is a problem which costs businesses millions of dollars annually as a result of time lost and production. New and better treatment solutions are always sought after in the hope of minimizing the economical influence this issue causes.  Men and women from all corners of the world suffer the pain of foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In a lot of these situations Shoe Lifts might be of very beneficial. The lifts are capable of easing any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless qualified orthopaedic practitioners". In order to support the human body in a healthy and balanced fashion, your feet have got a critical function to play. Irrespective of that, it is often the most overlooked region of the body. Some people have flat-feet meaning there may be unequal force placed on the feet. This causes other parts of the body such as knees, ankles and backs to be affected too. Shoe Lifts guarantee that proper posture and balance are restored. There are actually two unique variations of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital indicates you are born with it. One leg is structurally shorter compared to the other. Through developmental periods of aging, the brain picks up on the stride pattern and recognizes some difference. The body typically adapts by dipping one shoulder to the "short" side. A difference of less than a quarter inch isn't blatantly uncommon, demand Shoe Lifts to compensate and commonly does not have a serious effect over a lifetime.
 Leg length inequality goes largely undiscovered on a daily basis, however this problem is easily solved, and can reduce numerous cases of back pain. Treatment for leg length inequality usually consists of Shoe Lifts. These are generally very reasonably priced, usually costing below twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 and up. When the amount of leg length inequality begins to exceed half an inch, a whole sole lift is generally the better choice than a heel lift. This prevents the foot from being unnecessarily stressed in an abnormal position. Upper back pain is easily the most widespread ailment impacting men and women today. Around 80 million people suffer from back pain at some stage in their life. It is a problem which costs employers millions of dollars year after year due to lost time and productivity. Fresh and improved treatment methods are continually sought after in the hope of decreasing the economical influence this issue causes.  Men and women from all corners of the world experience foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In most of these cases Shoe Lifts can be of very useful. The lifts are capable of eliminating any pain in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by numerous expert orthopaedic physicians. To be able to support the body in a nicely balanced fashion, your feet have a very important job to play. Despite that, it's often the most overlooked zone in the body. Many people have flat-feet meaning there is unequal force exerted on the feet. This will cause other areas of the body including knees, ankles and backs to be affected too. Shoe Lifts make sure that ideal posture and balance are restored. .jpg) Overview OverviewHammertoes usually start out as mild deformities and get progressively worse over time. In the earlier stages, hammertoes are flexible and the symptoms can often be managed with changes in shoe styles and foot care products. But if left untreated, hammertoes can become more rigid and painful. Corns are more likely to develop as time goes on-and corns never really go away, even after trimming. In more severe cases of hammertoes, corn lesions may evolve into severe ulcerations. These lesions frequently occur in patients who have vascular disease or are Diabetic with neuropathy. The ulcerations can extend to the bone and result in infection and possible loss of digit or amputation. Causes Ill-fitting shoes or a muscle imbalance are the most common causes of Hammer Toe. If there is an issue with a muscle in the second, third or fourth toes preventing them from straightening, Hammer Toe can result. If one of these toes is bent long enough in one position, the muscles tighten and cannot stretch out. Left untreated, surgery may be required. Women are especially prone to developing Hammer Toe because of their shoes. Hammer Toe results from shoes that don?t fit properly. Shoes that narrow toward the toe, pushing smaller toes into a bend position for extended periods of time. High heels that force the foot down into a narrow space, forcing the toes against the shoe, increasing the bend in the toe.  Symptoms SymptomsPain on the bottom of your foot, especially under the ball of your foot, is one of the most common symptoms associated with hammertoes. Other common signs and symptoms of hammertoes include pain at the top of your bent toe from footwear pressure. Corns on the top of your bent toe. Redness and swelling in your affected area. Decreased joint range of motion in your affected toe joints. Diagnosis The exam may reveal a toe in which the near bone of the toe (proximal phalanx) is angled upward and the middle bone of the toe points in the opposite direction (plantar flexed). Toes may appear crooked or rotated. The involved joint may be painful when moved, or stiff. There may be areas of thickened skin (corns or calluses) on top of or between the toes, a callus may also be observed at the tip of the affected toe beneath the toenail. An attempt to passively correct the deformity will help elucidate the best treatment option as the examiner determines whether the toe is still flexible or not. It is advisable to assess palpable pulses, since their presence is associated with a good hammertoes prognosis for healing after surgery. X-rays will demonstrate the contractures of the involved joints, as well as possible arthritic changes and bone enlargements (exostoses, spurs). X-rays of the involved foot are usually performed in a weight-bearing position. Non Surgical Treatment The most common treatment is to wear more comfortable shoes. When choosing a shoe, make sure the toe area is high and broad and has enough room for hammer toes. If there is chronic pain, surgery may be needed to correct a malalignment. Surgical treatments are aimed at loosening up the contracted toe joints to allow them to align properly. Other types of treatment are products designed to relieve hammer toes, such as hammer toe crests and hammer toe splints. These devices will help hold down the hammer toe and provide relief to the forefoot. Gel toe shields and gel toe caps can also be used. Gel toe shields and toe caps will help eliminate friction between the shoe and the toe, while providing comfort and lubrication. Surgical Treatment Bone-mending procedures realign the contracted toe by removing the entire deviated small joints of the toe (again, not at the ball of the foot). This allows for the buckled joint to be positioned flat and the bone ends to mend together. Often surgical hardware (fixation) is necessary to keep the bones steady during healing. Hardware options can involve a buried implant inside the toe, or a temporary wire that is removed at a later date. Medical terminology for this procedure is called a proximal interphalangeal joint arthrodesis (fusion), or a distal interphalangeal joint arthrodesis (fusion), with the former being performed in a high majority of cases.
Overview
 A bunion is a bony growth in the lower joint of your big toe. It usually forms where the big toe pushes over against the second toe, forcing the joint to stick out. As a weight-bearing joint, this can be extremely painful. Calluses and blisters can form on the edge of the bunion, doubling the pain. This crippling foot affliction usually gets worse with time. Surgery for bunions can be complicated, expensive, painful and does not guarantee a well-formed foot as the outcome. A bunion is a bony growth in the lower joint of your big toe. It usually forms where the big toe pushes over against the second toe, forcing the joint to stick out. As a weight-bearing joint, this can be extremely painful. Calluses and blisters can form on the edge of the bunion, doubling the pain. This crippling foot affliction usually gets worse with time. Surgery for bunions can be complicated, expensive, painful and does not guarantee a well-formed foot as the outcome.Causes Long periods of pressure from a tight-fitting shoe can cause the inflammation and the pain. This often happens when the big toe is forced into a position where it presses inward and overlaps the second toe. The base of the big toe then is pushed beyond normal alignment of the foot, resulting in the prominence typical of a bunion. Symptoms Patients with bunions will often display pain over the prominent bump on the inside of their forefoot (the medial eminence?). However, they may also have pain under the ball of the foot (under the area near the base of the second toe). Symptoms can vary in severity from none at all to severe discomfort aggravated by standing and walking. There is no direct correlation between the size of the bunion and the patient?s symptoms. Some patients with severe bunion deformities have minimal symptoms, while patients with mild bunion deformities may have significant symptoms. Symptoms are often exacerbated by restrictive shoe wear, particularly shoes with a narrow toe box or an uncomfortable, stiff, restraining upper. Diagnosis The doctor considers a bunion as a possible diagnosis when noting the symptoms described above. The anatomy of the foot, including joint and foot function, is assessed during the examination. Radiographs (X-ray films) of the foot can be helpful to determine the integrity of the joints of the foot and to screen for underlying conditions, such as arthritis or gout. X-ray films are an excellent method of calculating the alignment of the toes when taken in a standing position. Non Surgical Treatment The initial treatment of a bunion should be non-operative. Symptoms can often be greatly improved with simple non-operative interventions. Non-operative treatment may include properly fitted shoes, Properly fitting comfort shoes with a wide non-constrictive toe box, especially one that is made out of a soft material such as leather, can be quite helpful in reducing the irritation over the prominent bunion. In some instances, it is helpful to have a shoemaker stretch the inside aspect of the shoe. Jamming a foot with a bunion into a constrictive shoe will likely lead to the development of uncomfortable symptoms. Bunion pads, Medial bunion pads may also be helpful in decreasing the symptoms associated with the bunion. These pads can be obtained at many drugstores. Essentially, they serve to lessen the irritation over the medial prominence and, thereby, decrease the associated inflammation This should be combined with comfortable non-constrictive shoes. A toe spacer placed between the great toe and the second toe can help to reduce the bunion deformity and, thereby, decrease the stretch on the medial tissue and the irritation associated with the bunion. Toe spacers can be obtained at most drug stores or online. Soft shoe inserts. Over-the-counter accommodative orthotics may also help bunion symptoms. This product is particularly helpful if bunion symptoms include pain that is under the ball of the foot. Orthotics with a slight medial longitudinal arch may be helpful for patients that have associated flatfoot deformity. These can be purchased at many sports stores, outdoors stores, or pharmacies. Bunion splints have often been used to treat the symptoms associated with hallux valgus. These splints are typically worn at night in an effort to reduce the bunion deformity. There is no evidence to suggest that these splints decrease the rate at which bunion deformities occur. There is also no evidence that clearly supports their effectiveness. However, some patients report good relief with the use of these splints. 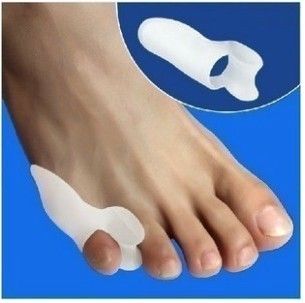 Surgical Treatment For severe bunions, outpatient surgery may be recommended. Within hours after surgery, you?ll be on your way home and ready for recovery. Your foot will be bandaged following surgery and placed in a surgical shoe which allows you to remain mobile. Immediate weight bearing without the use of casting or crutches is standard post- operative recovery for bunions. In most cases, the majority of healing should occur within a few weeks and you can resume normal activity within a short period of time. Bunion surgery can both reduce pain and improve the appearance of your feet. After surgery it is important to see your podiatrist as scheduled and follow all recovery instructions. |
|
